Vietnam has been one of the fastest growing economies in Asia the past 30 years bringing it from poverty to a lower middle income country. Before Political and economic reforms launched in 1986, Vietnam was one of the poorest in the world, with per capita income around US $100. By the end of 2015, Vietnam is a lower middle income country with per capita income of around US$2,100, thanks to the average per capita GDP growth of 6.4% in the 2000s.
| Area | 332,698 sq km |
| Population | 91.7 mil. (2014), Population in working age: App. 77% (2014) |
| Capital city | Hanoi |
| Major cities | Ho Chi Minh City, Da Nang, Binh Duong, Hai Phong |
| Government | Socialist one-party state |
| Language | Vietnamese |
| GDP | GDP $214,750 BUSD (2015 est.) GDP per capita: 2,321 USD |
| FDI 2014 | USD 20.2 bil. More than half from South Korea, Hong Kong and Singapore |
| Unemployment | 2.3% (2015 est.) |
| Minimum wage | $107-156 USD per month, depending on regions |
| Tax rate | Corporate tax 20% since 1 Jan, 2016 , VAT 10% |
| Public debt | 50.5 % of GDP (2014 est.) |
| Inflation rate | 0.63% (2015 est.) |
| Export | 150 BUSD (2014 est.) |
| Import | 148 BUSD (2014 est.) |
Advantages of the economy
Political and social stability
Vietnam with reform commitment and stable political situation makes it one of the safest investment destinations in Southeast Asia. This helps the government to promote Vietnam as an investment avenue and ensuring economic development.
Strategic location
Vietnam’s proximity to China and ASEAN countries makes it a potentially trading partner with these countries.
Growing economy
Vietnam has experienced an impressive growth over the last few decades, only second to China. Vietnam’s GDP has grown about 10 times from that in 1991, from approximately US$14 billion in 1991 to approximately US$138 billion in 2012.
Urbanisation
Fast urbanisation rate with large infrastructure investments, emerging middle class, though remain competitive low labor cost compared to neighbouring countries makes Vietnam a potential big market as well as manufacturing hub.
Challenges in the market
Although the business climate in Vietnam is improving all the time, obstacles still remain. The main restrain of doing business in Vietnam are inadequate infrastructure, weak legislation and policy transparency. Transparency International rated Vietnam 112th out of 168 in its Corruption Perceptions Index for 2015. Also, productivity is lower than some neighbouring countries. In particular, labor productivity in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines and Indonesia were 18, 6.6, 2.7, 1.8 and 1.8 times higher than that of Vietnam in 2013. However, the labor productivity in Vietnam has increased quite fast in recent years thanks to the increasing young skilled labour force, which is a boost to the economic growth.
Key production hubs
North Vietnam, Hanoi is the political center. The North is also becoming an industrial hub for heavy manufacturing activities
Central Vietnam (IT & Tourism) Da Nang, a dynamic emerging city in Central Vietnam, is ranking high in high tech development and IT infrastructure. It is also a popular tourist spot.
South Vietnam (Financial and Commercial center) Ho Chi Minh City is the commercial hub, the financial center and headquarters of many foreign and Vietnamese private companies.
Key sectors for EU business
Vietnam is an attractive alternative to China and India due to rising costs and attrition rates. This is due to the increasing costs of labor in China; rising Chinese taxes on foreign enterprises and difficulties with the business environment in China. Political stability, giant infrastructure investments, abundant workforces with low salary and a new emerging middle income class makes Vietnam attractive to new investors with the following opportunities
- Garment, textile and leather sourcing
- Furniture sourcing
- Software outsourcing
- Healthcare – Pharmaceutical & Medical Device
Vietnam Top Export Goods 2015
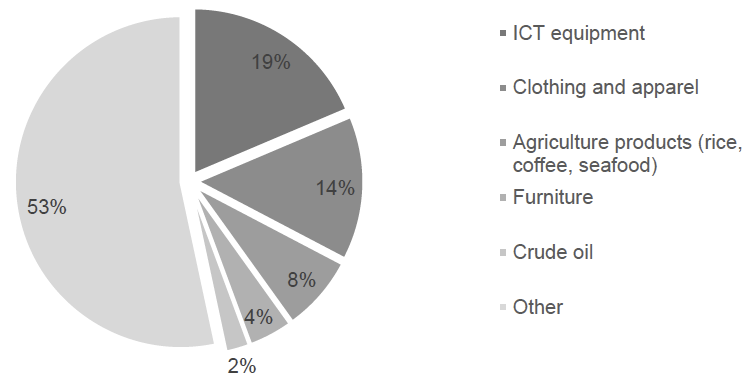
In 2015, ICT equipment contributed $30.18 billion USD in the total export of $162 billion USD, comprised 19%. However, the majority of export value came from FDI, with about 90% value from Samsung.
Clothing and apparel, agricultural products and furniture are among the top export with value of $22.81 billion USD, $12 billion and $6.9 billion USD respectively, corresponding to 14%, 8% and 4%.
Rising Stars in Southeast Asia – Business Opportunity Analysis